So you have a problem at work you need to solve.
Maybe your team’s struggling to make sense of information when it’s spread across different platforms and communication channels. Maybe you need a single place to coordinate logistics and manage attendees for your company’s annual conference. Or maybe you’re finding it hard to keep track of inventory levels, leading to overstock or stockouts.
There’s an app for that.
And it might be the one you build yourself—without writing a single line of code.
No code app builders give employees and founders the power to solve their problems themselves, without needing deep pockets or expert technical knowledge. Thanks to their ease of use and ability to solve a myriad of problems, the use of no code apps in the business world is growing. Gartner estimates that organizations will build 70% of their new applications with low code or no code tools by 2025, a significant increase from less than 25% in 2020.
With so many options available, let’s break down what a no code app builder is and how to choose the right one.
What is a no code app builder?
A no code app builder is a tool that lets you create applications without writing code. You can connect your data to your app and use drag-and-drop functionality—or a WYSIWYG editor—to visualize and customize it. Depending on the features you add, you can also add or edit data directly from your app as well as from your data source.
There are different types of no code app builders for different purposes. Some have easy learning curves, but limited features and data sources, making them suitable for those who want to build personal apps. Others help entrepreneurs build mobile apps to sell on the iOS App Store, Google Play Store, or as a web app for a SaaS product. Some application development platforms fall more in the domain of low code builders, meant for programmers who need a low code platform to speed up the development process.
And some are mainly designed to help businesses build powerful internal business tools such as knowledge management systems, product inspection tools, and property management hubs. Using no code app builders gives you an impactful way to create custom apps that solve your business problems, at a fraction of the cost of traditional development.
Here are some questions to ask when choosing the best no code app builder for your business.

The Ultimate Guide to No Code
Read now1. What are your business’s needs?
First and foremost, think about all the things you need to accomplish with the app you want to build.
Problem to solve—Think about the problems your business is currently facing that you need a good solution for. What processes are causing your team pain, what tools are causing disconnection or siloing information, and where are you not able to use data effectively? These could be anything from inefficient workflows to disorganized data to disjointed communication—or multiple problems at the same time.
How quickly you need to solve it—One of the appealing aspects of no code is how fast it can get you from idea to app compared to traditional development. Some no code tools can help you get moving as fast as possible while maintaining the reliability of your data wherever it lives, while others might take a little longer to get you off the ground, depending on their complexity at the back end. This is something you’ll have to consider when choosing a no code app builder.
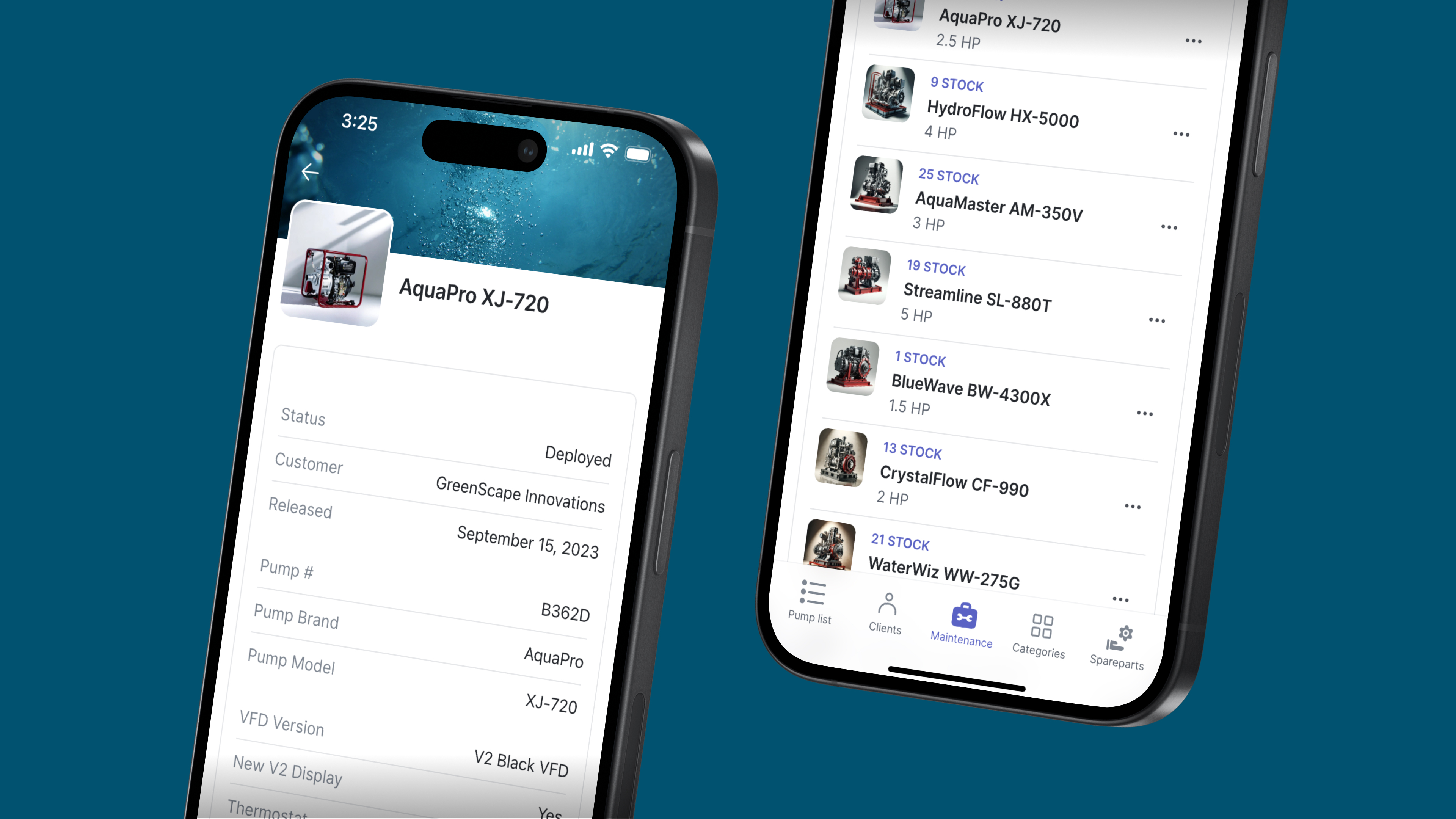
What type of app you want to build—App builders can build two types of apps - progressive web apps (PWAs) or native apps. PWAs can be accessed on any device through your browser, so users can access the same app on a laptop, tablet, or smartphone. Native mobile apps are mobile-only and device-specific - they must be downloaded from the Google Play or Apple App Store. They also need to be made separately for iOS or Android operating systems. The convenience of using PWAs from any device makes them suitable for your team to use to access data or for customers to use to easily interact with your business. Native apps, on the other hand, are well suited for creating products for public use. Once you’ve identified which type of app you need, look for a vendor that lets you build it. Bubble is a popular native app builder for SaaS startups, while Glide is mainly focused on creating PWAs, making it the ideal choice for building business tools.
Future needs—You know what you want to build today, but is there a chance you might need more internal apps in the future, either for other teams or other use cases? Look for a vendor that lets you scale easily (both in terms of data volume, user volume, and number of apps) while being cost-effective.
Who will be using the app—Your app should be intuitive for the people it’s meant to help, whether they’ll be adding data to it, accessing data, or both. Are the app builder’s features and usability catered to both types of users? For example, if you’re building an internal knowledge base, someone on your team will have to set it up in the back end first by pulling in data, setting up organizing logic, and creating systems for the rest of the team to access the data and add to it from the app’s user interface. The tool you choose should be user-friendly for both types of users.
“What I like about Glide is that it puts your data into a really nice configurable user interface and makes it more intuitive to people,” he said. “It caters really nicely to user-generated data, which we have a lot of.” – Marc Walford, Head of FinOps at ITV
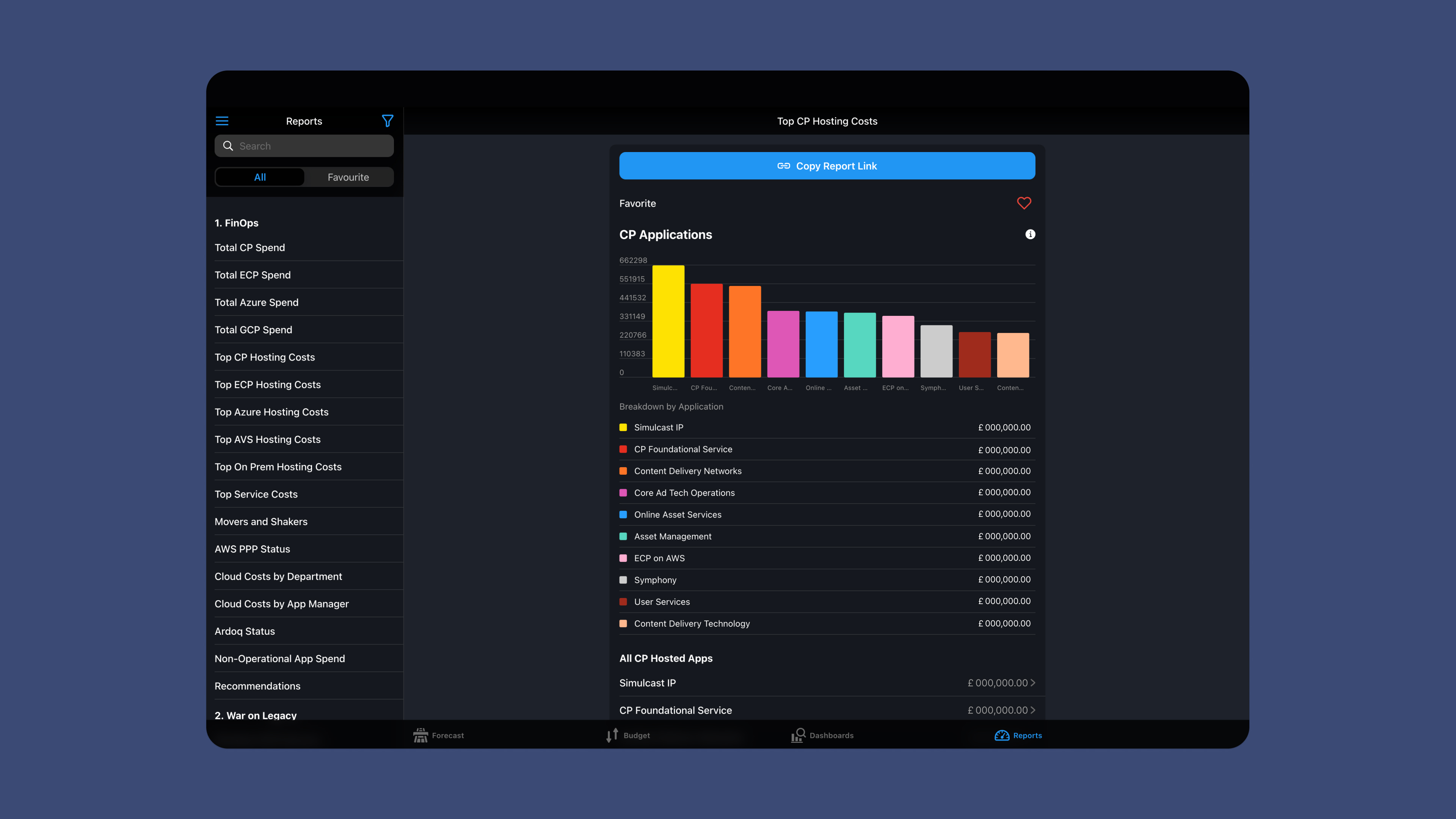
2. What is your current system for data organization and workflows?
A Forrester study found that organizations use, on average, 259 apps and systems, leaving employees spending nearly two and a half hours every day trying to find information. Even if your organization’s data isn’t spread across hundreds of tools, it likely lives in more than one place. These data sources could be anything from Google Sheets or Airtable to SQL databases or locally stored files.
Consider the data you use every day. Is it stuck in spreadsheets, inaccessible, inconvenient to work with, or all of the above? Make a list of all the tools you use, what data they hold, and where they’re disconnected. Customer information may be in your customer relationship management (CRM) system, financial data in accounting software, inventory details in a warehouse management system, and communication in email. Compare your data sources to those available in the no code app builder to find one that supports the data sources you need.
Softr is a popular no code builder with limited data sources, making it suitable for building personal apps. Glide connects to a wide range of data sources and SQL databases, making it suitable for businesses that need to bring data from disparate sources into a central location. Microsoft PowerApps and Airtable let you create interfaces that mainly work with only a single data source, making them most suitable for users who are fully integrated with Microsoft Excel or Airtable, respectively, and don’t need too much data flexibility.
“We went from a bunch of data sources (Excel) that didn't match, to a unified data source that did. One source of truth—and then the teams all viewed and updated that same source going forward.” — Bill Schonbrun, COO and Co-Founder of CarboNet
Then, look at how your team currently tries to connect data from these different sources and identify workflows that are slow, laborious, or prone to errors. Integrations that connect your internal business app to other tools can help streamline workflows, reduce manual errors, and save time, allowing your team to focus on more strategic tasks.
Check if the app builder has integrations with third-party services you use, and if it has an API that lets you connect with other tools. For example, you could build a custom app that sends push notifications to a specific team member’s device when something urgent needs their attention. Or you could set up an integration enabling your team to generate PDFs of monthly client billing statements.
3. Is it easy to learn and use?
No code can help you create powerful apps, and while it doesn't require coding knowledge, there’s still a learning curve as you get familiar with the app builder’s interface. Some platforms, even purely no code ones, are more challenging to learn than others.
Before you go further, check if the platform you’re considering is low code or no code. They sound similar, but they aren’t the same. Low code app development platforms are designed to help technical teams (or people with some technical knowledge) build apps using drag-and-drop functionality combined with custom code. No code development platforms are designed for anyone to use, whether or not they have coding skills. The platform’s website will usually specify whether it’s low code or no code.
Look at the resources the vendor provides to help you learn how to use the no code platform. These could be one or more methods, including video tutorials, templates for hands-on learning, product certification, an updated knowledge base, and a strong community.
4. How complex do you need it to be?
No code can help you build simple apps, like an employee leave management system. It can also handle more complex apps, such as an inventory and supply chain management system that covers inventory tracking, order management, supplier management, warehouse management, and even demand forecasting.
Think about what you’re building and what features it’ll take to create it. Do you need an app that handles large volumes of data? Do you need an app interface that enables users to only view the data or also add to it without accessing the back end? How about automating certain processes and integrations with other tools?
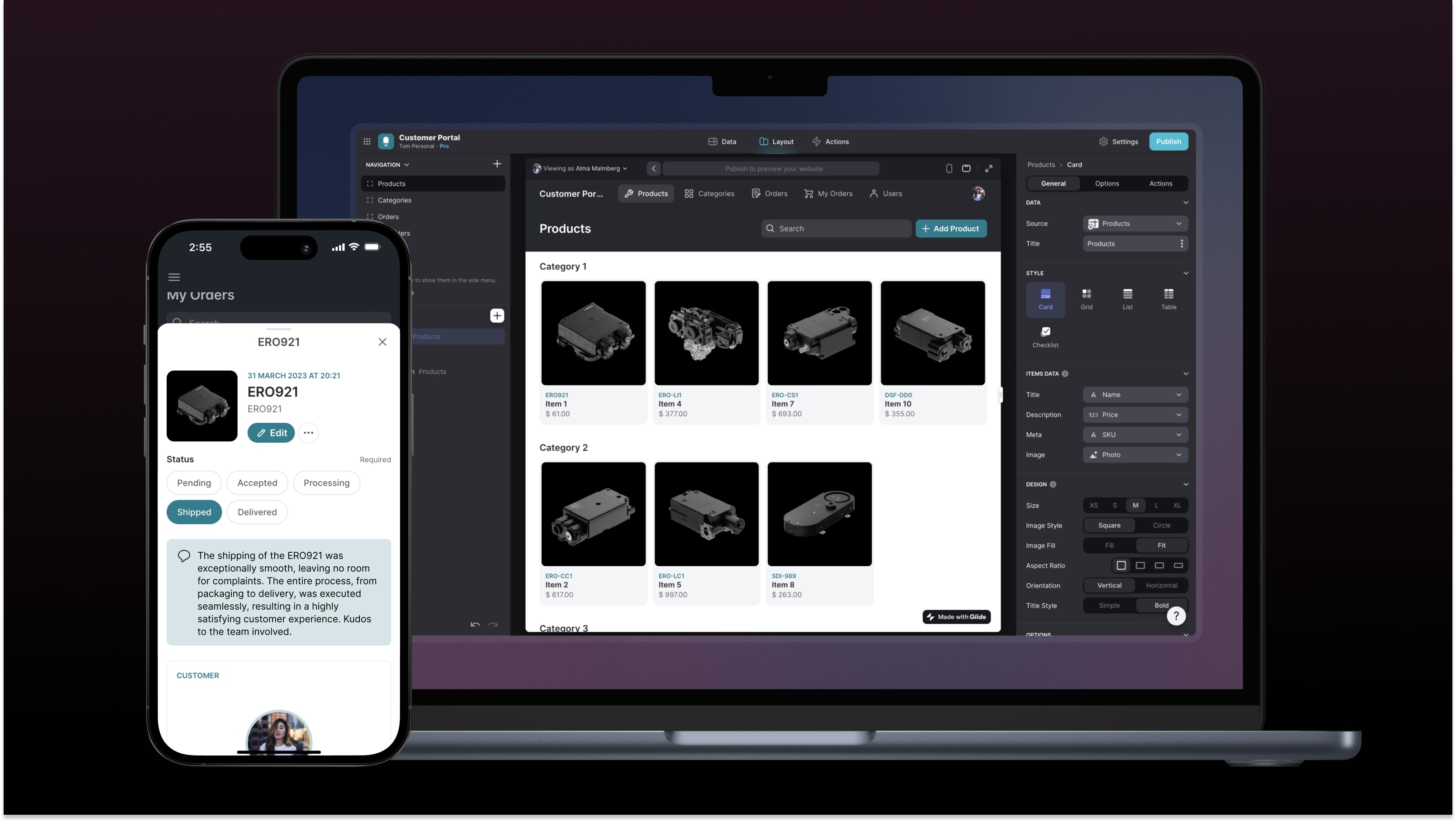
It’s easy to get overwhelmed with features you don’t need—and perhaps pay a premium for features you won’t use—or to commit to an app builder only to find it doesn’t have some features your app needs to function. Compare the features you need to what the no code tool offers. App builders like Glide can handle data, interfaces, and automations, offering a versatile solution for internal business apps across your organization. On the other hand, Bubble has SEO capabilities to help search engines find and index apps, which isn’t necessary for internal apps but can help external apps capture search engine traffic.
5. What design features does it have?
Good design is about more than aesthetics—it creates a better user experience, which can encourage your team to use the app more. Since PWAs can be accessed on any web and mobile device, they need to provide a good user experience on computers, tablets, and smartphones. Verify that the no code app creator uses adaptive design. This feature means that you design once, for the screen of your choice, and the tool adapts your app to work across all devices. Without it, you’d have to design the app separately for different screen sizes, increasing the time taken to create the app and the risk of providing users with an inconsistent experience on different devices.
Weigh the mobile app builder’s flexibility in customization options against the amount of effort needed to create an effective design. Glide has adaptive design and a more constrained design system that makes it easy to create professional-looking and feeling apps, great for both internal and customer-facing apps. Microsoft PowerApps has a looser design system with more customization, but that can also make it hard to create a truly polished-looking app if you don’t have design support on your team. If you’re building a native app that’s customer-facing, look for a design-forward platform that helps you build beautiful and functional apps.
6. How does it use AI?
AI can speed up your workflows and bring advanced functionality to your app. Look at the different ways the no code app builder supports AI to see if any of these are applicable to the app you’re building. For example, if you’ve integrated your app with a customer support tool, can your no code app builder use AI to conduct sentiment analysis and flag tickets that need a follow-up? For teams that upload digital scans of paperwork or receipts, does your app creator include Optical Character Recognition (OCR) to extract text from images?
7. What is the pricing model?
Compare your budget to the app builder’s pricing model to evaluate if it works for you or is too costly. When considering your options, here are some aspects to evaluate that relate to pricing:
Features—Many no code app builders have a tiered pricing structure, with more features and integrations included at higher plans. Does it have the features you need at a pricing plan that suits your budget, or do you need a higher plan that might derail it? For example, Softr defaults to web applications, so if you want a mobile application, you’ll have to pay for a more expensive plan. Glide and Adalo both support mobile apps at lower pricing tiers.
Number of apps—Evaluate how many apps you need to build—now or in the future—and which app builder’s pricing model works best for these needs. Bubble and Adalo are priced per app, so they may be suitable options if you need to build only one app. Glide has no limit on the number of apps businesses can build, so it’s the better choice if you want to build multiple apps for your team.
Number of users—Your whole team needs to use your internal business app so that everyone has access to the same data. Will you be charged by license for each individual user, including external users or guests? This could add up quickly as your team grows or you need to add more guests, such as tenants for a work order maintenance app. App builders such as Microsoft PowerApps and Google AppSheet charge a fee per user, which may not be suitable for large teams or businesses with multiple guest users.
8. Does it have experts who can help you build your app?
One of the advantages of no code is that it empowers non-technical users to create their own apps. For more complex projects and workflows, or if you just want to move as fast as possible without taking precious time away from your team, you may want the assistance of an expert who can help you with an app you’ve already built, help you as you build, or build the entire app for you.
Some no code app builders run programs for no code developers where they vet consultants and agencies that are certified to build apps on their platform. They provide the experts with training and resources to support organizations in building no code apps that solve business problems. Glide Experts are no code developers with in-depth knowledge of and extensive experience with using Glide for a wide range of use cases, from scaling field operations to going paperless with an AI-powered app.
9. What other features does it have?
No code app builders can be packed with features, and it’s impossible to list them all. Identify what you want to do with the app, and the features you need to do it, before you check all the features the app builder provides.
Do you need to scan tickets for an event or products for inventory? You’ll need a barcode scanner.
How about improving the user experience for team members, customers, or clients who are fluent in other languages? Localization is the answer.
Maybe you’re an e-commerce business that wants to avoid stockouts? Real-time push notifications can alert your team when stock levels are low.
No code apps can achieve many outcomes, so look for an app builder that supports you in accomplishing your specific goals.
Are no code app builders any good?
The short answer is yes. Very. As no code technology has matured, no code app builders are becoming an essential part of a modern digital business.
No code app builders empower teams to innovate quickly without requiring extensive coding knowledge, making them a valuable tool for many modern businesses. They can help you create powerful apps that simplify processes, provide employees with tools that fit their specific needs and workflows, and centralize data management. These are just a few benefits of using no code app builders for your business.
While no code app builders might not be perfect for everyone—especially businesses with strict security and compliance needs or those requiring highly specialized coding for mobile games or advanced interactive elements—the vast majority of businesses will find them incredibly useful. For most use cases, the ease of use, speed of development, and cost savings make no code app builders like Glide an excellent choice for solving your business problems.

Shivani Shah is a writer, editor, and content marketing consultant who likes to make complex ideas easy to understand. She believes in "show, not tell" and works with B2B tech companies, helping them highlight how their products can solve customer problems. Her areas of expertise include community management and data privacy.




